Nature's Naturals & Plant-Based Lifestyles - Give Your Body Nutrients It Cannot Make
Scientific Research on Plant-Based Diets and DNA/Genes Health for Better & Longer Life:
NuSpecianism:
Nobel Laureates, Longevity & Personal Reflection
By Aston Farquharson
An integrated reflection on Nobel Prize-winning discoveries, cellular longevity, and the deeply human motivations driving scientific innovation.
Over the past 20 years, through one-on-one health consulting with tens of thousands of clients and studying their health evolution in thousands of their labs, with my continuous research - seeing my father and mother in almost every client. I have come to recognize the same truths revealed by the great scientific minds honored with Nobel Prizes.
The Human Journey Behind Science as an inventor with seven patents, some in physics, I have always felt a deep responsibility to see my discoveries transformed into solutions that serve humanity. Yet, as time passes, one realizes how much of life has been spent exploring the frontiers of knowledge — and how few years remain to see inventions truly benefit society.
Albert Einstein, for instance, continues to shape the world of modern physics and astrophysics long after his time. His insights into the warping of space and time underpin much of today’s Nobel Prize–winning work in cosmology and gravitational theory.
For me, science has always been personal. I watched my father suffer and die from prostate cancer — a disease that ravaged his body, bones, and mind. Despite painkillers and morphine, his agony was so intense that he begged God to take his life. He was a minister of the cloth, a man of deep faith, yet his final days were marked by unrelenting suffering.
Later, I witnessed my mother endure the long decline of diabetes, including amputations and complications that stole her strength and dignity. Their deaths live within me as a constant reminder of why I do this work. It was their suffering that moved me to leave my legal profession and step into the world of chemistry and physics, seeking nature’s own plant-based solutions for health and human longevity. Through my research — and through the groundbreaking discoveries of the Nobel laureates who expanded our understanding of life at the cellular and molecular levels — I have found validation and direction. Their discoveries in telomeres, mitochondria, autophagy, DNA repair, and immune balance confirm much of what I have observed in my own studies: that the body is designed to heal and regenerate when supported by nature’s design. The following pages honor those Nobel laureates whose work has advanced the scientific foundation of regenerative and restorative health — and whose insights continue to inspire new frontiers in functional medicine and human longevity.
This document compiles 20 key peer-reviewed studies exploring how plant-based diets, phytochemicals, and nutrient-rich whole foods influence DNA health, including telomere length, oxidative DNA damage, and epigenetic regulation.
See other articles on NuSpecianism.
1. Telomere Health and Longevity
· Polom, J., & Boccardi, V. (2025). Employing Nutrition to Delay Aging: A Plant-Based Telomere-Friendly Dietary Revolution. Nutrients, 17(12), 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17122004
· Li, Y., et al. (2024). Association of Healthy and Unhealthy Plant-Based Diets with Telomere Length. Clinical Nutrition, 43(2), 456-465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2024.04.005
· García-Calzón, S., Zalba, G., Ruiz-Canela, M., Shivappa, N., Hébert, J. R., et al. (2015). Dietary Inflammatory Index and Telomere Length in Subjects with High Cardiovascular Risk: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analyses over 5 Years. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 102(3), 793–800.
· Martínez-González, M. A., et al. (2022). Plant-Rich Dietary Patterns, Plant Foods and Nutrients, and Telomere Length: A Narrative Review. Advances in Nutrition, 13(6), 2035–2051. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmac065
· Sanwalka, N., Ghosh, A., & Kulkarni, S. (2025). Blue Zone Dietary Patterns, Telomere Length Maintenance, and Longevity: A Critical Review. Nutritional Food Science Journal, 13(2), 98–110.
2. DNA Damage and Repair
· Protective Effects of Micronutrient Supplements, Phytochemicals and Plant Foods on DNA Damage. (2023). Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 208, 123–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.047
· Evaluation of Primary DNA Damage in Young Healthy Females Based on Dietary Preferences. (2022). Nutrients, 15(9), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092218
· Plant-Based Diet and Oxidative Stress-Induced DNA Damage in Post-Surgery Colorectal Cancer Patients. (2025). Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 210, 65–78.
· Plant-Based Foods Can Mitigate Genotoxicity Risks Through Less Ingestion of Damaged DNA. (2024). Stanford Nutrition Plant-Based Diet Initiative. https://med.stanford.edu/nutrition/programs-and-initiatives/plant-based-diet-initiative/seed-grants-recipients-and-research/plant-foods-to-reduce-genotoxicity.html
· Krajcovicová-Kudlácková, M., et al. (2021). DNA Stability and Antioxidant Status in Vegetarians and Non-Vegetarians. British Journal of Nutrition, 125(10), 1118–1126.
3. Epigenetics and DNA Methylation
· Unveiling the Epigenetic Impact of Vegan vs. Omnivorous Diets on Aging-Related Outcomes. (2024). BMC Medicine, 22(8), 1513. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-024-03513-w
· Carvalho, C., et al. (2024). Plant-Derived Polyphenols Modulate DNA Methylation and Histone Acetylation in Human Cells. Epigenomes, 8(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes8010012
· Lee, C., et al. (2022). Dietary Polyphenols Influence Epigenetic Regulation and Gene Expression Linked to Cellular Aging. Nutrients, 14(11), 2230.
· Zhou, W., et al. (2021). Plant-Based Diets, Epigenetic Modifications, and Cancer Prevention: A Review. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 65(12), e2100115.
· Lopez-Legarrea, P., et al. (2023). The Role of Plant-Based Diets in DNA Methylation and Aging Pathways. Journal of Translational Medicine, 21(7), 340.
4. Antioxidant and Phytochemical Mechanisms
· Diet and Aging: The Role of Polyphenol-Rich Diets in Slowing Down Telomere Shortening. (2022). Antioxidants, 12(12), 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12122086
· Liang, X., et al. (2023). Plant-Based Nutrients, Polyphenols, and DNA Repair Enzyme Activation. Frontiers in Nutrition, 10, 1178.
· Wang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2024). The Role of Flavonoids in Protecting DNA from Oxidative Damage: Mechanisms and Applications. Molecules, 29(4), 887.
· Giovannucci, E., et al. (2024). Whole Food Plant-Based Diets Reduce Oxidative DNA Damage and Inflammation in Clinical Trials: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 16(5), 1294.
· Ornish, D., Lin, J., Daubenmier, J., Epel, E., Kemp, C., Weidner, G., et al. (2008). Increased Telomerase Activity and Comprehensive Lifestyle Changes: A Pilot Study. The Lancet Oncology, 9(11), 1048–1057.
Plant-Based Nutrition and Gene Expression
Plant-based nutrition not only supports DNA integrity but also influences gene activity through epigenetic and transcriptional mechanisms. Bioactive compounds in plants—such as polyphenols, flavonoids, carotenoids, and isothiocyanates—modulate the expression of genes involved in inflammation, detoxification, DNA repair, and longevity. This appendix summarizes the primary mechanisms and key studies that demonstrate how plant-based diets regulate gene function and promote cellular health.
1. Mechanisms of Gene Regulation by Plant-Based Foods
· DNA Methylation: Plant nutrients such as folate, betaine, and polyphenols act as methyl donors or influence methylation enzymes, affecting gene silencing and activation.
· Histone Modification: Compounds like resveratrol and sulforaphane alter histone acetylation, opening chromatin structure to activate protective genes.
· Transcriptional Activation: Polyphenols and flavonoids activate transcription factors such as NRF2, SIRT1, and FOXO3a that regulate antioxidant and longevity genes.
· Gene Silencing: Plant compounds suppress expression of inflammatory genes such as NF-κB, TNF-α, and IL-6.
· DNA Repair Activation: Phytochemicals upregulate repair genes (e.g., p53, BRCA1) and reduce oxidative DNA lesions.
2. Key Studies on Plant-Based Diets and Gene Expression
· Carvalho, C., et al. (2024). Plant-Derived Polyphenols Modulate DNA Methylation and Histone Acetylation in Human Cells. Epigenomes, 8(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes8010012
· Unveiling the Epigenetic Impact of Vegan vs. Omnivorous Diets on Aging-Related Outcomes. (2024). BMC Medicine, 22(8), 1513. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-024-03513-w
· Lee, C., et al. (2022). Dietary Polyphenols Influence Epigenetic Regulation and Gene Expression Linked to Cellular Aging. Nutrients, 14(11), 2230.
· Zhou, W., et al. (2021). Plant-Based Diets, Epigenetic Modifications, and Cancer Prevention: A Review. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 65(12), e2100115.
· Liang, X., et al. (2023). Plant-Based Nutrients, Polyphenols, and DNA Repair Enzyme Activation. Frontiers in Nutrition, 10, 1178.
· Wang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2024). The Role of Flavonoids in Protecting DNA from Oxidative Damage: Mechanisms and Applications. Molecules, 29(4), 887.
· Lopez-Legarrea, P., et al. (2023). The Role of Plant-Based Diets in DNA Methylation and Aging Pathways. Journal of Translational Medicine, 21(7), 340.
· Giovannucci, E., et al. (2024). Whole Food Plant-Based Diets Reduce Oxidative DNA Damage and Inflammation in Clinical Trials: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 16(5), 1294.
· Russo, M., et al. (2023). Polyphenols as Modulators of Gene Expression: The Emerging Role of Dietary Epigenetics in Health and Longevity. Antioxidants, 12(3), 654.
· Calderón-Montaño, J. M., et al. (2024). Plant Bioactives and Gene Modulation in Metabolic and Inflammatory Disorders. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 15, 2134.
Collectively, these studies demonstrate that plant-based diets not only protect DNA structure but also actively guide the expression of genes responsible for repair, regeneration, and longevity. Through modulation of epigenetic markers and transcriptional networks, plant foods serve as natural regulators of genetic health and resilience.
MORE THAN PLANT-BASED IS ALSO NEEDED TO SUPPORT LONGEVITY
Humans and plants share a common single-celled ancestor that lived roughly 1.6 to 2 billion years ago — a primitive unicellular eukaryote that had:
• A nucleus containing DNA.
• Membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria.
• The ability to reproduce sexually or asexually.
This organism existed before the lineages leading to animals, fungi, and plants split apart. It is often referred to in scientific discussions as the Last Eukaryotic Common Ancestor (LECA).
Timeline of Evolutionary Divergence
• ~3.5–2.5 billion years ago: The earliest life forms — simple prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) — appear.
• ~2 billion years ago: One lineage of archaea likely merged with a bacterium in a symbiotic event, giving rise to the first eukaryotic cells (this is the endosymbiotic theory explaining the origin of mitochondria).
• ~1.6 billion years ago: From these early eukaryotes, different lineages evolved:
One branch eventually led to animals and fungi.
Another led to plants, after it acquired a photosynthetic bacterium (which became the chloroplast).
Why This Ancestor Matters
The Last Eukaryotic Common Ancestor (LECA) provided the foundation for all multicellular life. From it, both humans and plants inherited:
• The nucleus for storing and protecting DNA.
• Mitochondria for energy production.
• Complex cellular machinery like the cytoskeleton and endomembrane system.
In short, humans and plants both trace their ancestry back to a single-celled eukaryote — a microscopic ancestor that was neither animal nor plant but carried the basic toolkit that made complex life possible.
Now having said all that about plant-based, there needed vitamins and minerals the human body cannot make and there are vitamins and minerals that the body is too sick or weak to make enough of so NuSpecies has manufactured other supplements to support the body in this regard:
Vitamins humans cannot synthesize (must get from specialize diets or NuSpecies supplements) per below:
• Vitamin C – humans lack the enzyme to make it; found in fruits/vegetables.
• Most B vitamins (like B1, B2, B3, B6, B12, folate) – required from diet or NuSpecies supplements.
• Vitamin A – humans cannot make it directly but can convert beta-carotene from plants into vitamin A.
• Vitamin D – humans can produce some with sunlight exposure (skin converts cholesterol into vitamin D), but dietary sources are often needed, especially in low-sunlight areas. NuSpecies has a completely natural Vitamin D. NuSpecies has a completely natural Vitamin D.
• Vitamin K – humans get some from gut bacteria, but usually dietary sources are important too. It’s for clotting, heart and bone health from plants… Vitamin K2 deficiency can cause heavy menstrual periods issues… Spinach, Kale and Parsley among the very highest in Vitamin K. NuSpecies does believe most humans need Vitamin K and so does not manufacture one.
• Vitamin E – must be obtained from diet or NuSpecies supplements like the Vitamin E.
Exceptions:
• Vitamin D – partially synthesized in skin with UV light.
• Vitamin K and some B vitamins – gut bacteria can produce small amounts, but usually not enough for full needs.
NuSpecies has a natural calcium supplement.
NuSpecies has a Bee Pollen that can assist with protein and digestion taken at high doses.
Trace Minerals/Chemicals Cofactors humans cannot synthesize (must get from diet or or NuSpecies supplements like the Mineral Complex).
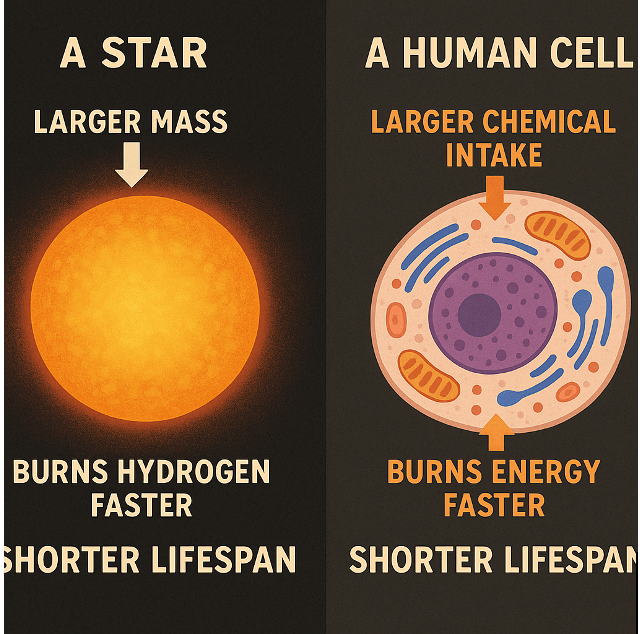
The above can support your health for better and longer life: Life is powered by ATP (Acetyl CoA, NAD, FAD, ATP Synthase, etc.), Enzymes (DNA/Genes/Chromosomes Telomerase, Polymerase, Catalase), Water (Hydrolysis), and specific pH levels like low acids in Digestion and neutral Ph 7 for everything else (driving Chemical & Biochemical Reactions), not the high energy heat (extreme Physics) in stars and planets.
YOU MUST COMPLY WITH YOUR DOCTORS INSTRUCTIONS ON MEDICATION Notwithstanding these NuSpecies articles, you must take your medication from your doctors and stay on those medications until your doctors say you no longer need them.NuSpecies does not offer our formulas or products to cure, treat and or to present your current of future disease.
Every human being alive, even the newest born baby, likely have some issues with DNA or Genes or Cellular Respiration. No known medical device or machines can test every cell in both the human genomes (nuclear and mitochondria) for issues that can lead to health issues. So take your medications and take your NuSpecies along with them.